MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel)
Purpose: Separate business logic, UI and data to improve testability and structure.
1. Model
- Represents the data and business logic.
- Example: Network responses, database entities, business rules.
2. View
- Represents UI components (like
UIViewController). - Displays data from the
ViewModel.
3. ViewModel
- Transforms data from the Model to a format the View can use.
- Contains logic to respond to user input and update the view.
- Binds to the View using Observables (like RxSwift, Combine or custom bindings).
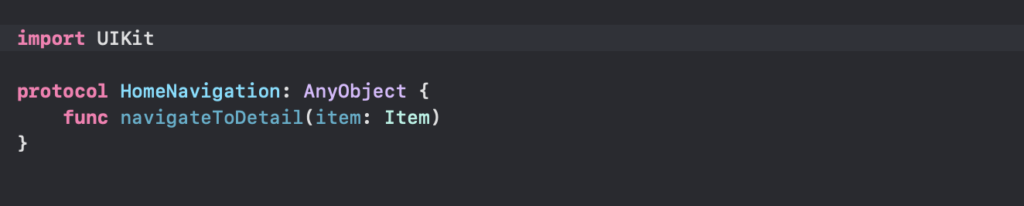
Coordinator Pattern
Purpose: Decouples navigation logic from view controllers. This helps to:
- Avoid massive view controllers
- Improve reusability and testability
- Centralize and control navigation flow
Coordinator Responsibilities:
- Handle navigation (push, pop, modal etc.)
- Own and start view controllers
- Communicate between modules